
What is Linear Guide Types and Materials Available
Publish Date: 6 Oct 2025
Linear guides are essential components that enable smooth, precise, and stable straight-line movement in machinery. They are widely used in automation, robotics, precision instruments, and heavy machinery due to their ability to reduce error, support high loads, and maintain long service life with minimal maintenance.
What is a Linear Guide?
A linear guide is a mechanical system consisting of a rail and a block (or carriage). The block slides along the rail with rolling elements (usually steel or ceramic balls) to reduce friction and ensure smooth movement. Unlike plain sliding systems, linear guides distribute loads evenly and maintain precise alignment, which makes them indispensable for precision engineering tasks.

Key Features of Linear Guides
- Precision motion with reduced vibration and noise
- Rails specified in 1 mm increments for custom designs
- Long service life with optimized load distribution
- Available in sets or separate parts (rail only, block only)
- Compatibility with peripheral accessories like stoppers, clamps, locks, and bellows
Types of Linear Guide Blocks
A variety of block (carriage) types, each designed for specific load and space conditions.
| Block Type | Description | Key Benefit | Typical Use | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
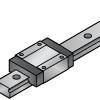 |
Standard | General-purpose block with balanced dimensions | Versatility & ease of design integration | Machinery with moderate loads |
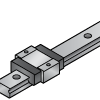 |
Short | Reduced length for compact installations | Saves space | Compact devices, instruments |
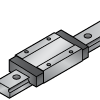 |
Long | Longer footprint for even load distribution | Stable motion & higher rigidity | Medium to heavy-duty machinery |
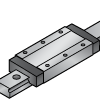 |
Extra Long | Extended length for maximum stability | Handles very high loads with precision | Press machines, cutting equipment |
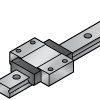 |
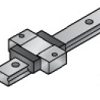
Wide | Wider block for increased lateral stability | Prevents tilting under side forces | Robotic arms, gantry systems |
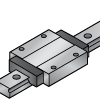 |
Wide Long | Combination of wide + long block | High stability for multi-directional loads | Heavy automation, CNC machines |
 |
Wide Short | Wide but compact | Balances stability with reduced footprint | Robotics in limited space |
Materials Available
| Material | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High strength, excellent rigidity, suitable for heavy industrial applications |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistance, suitable for clean rooms, medical equipment, and food-grade environments |
Types of Linear Guide Rails
| Rail Type | Description | Ideal Application | |
|---|---|---|---|
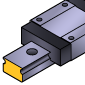 |
Standard Rail | Slim, compact design, general purpose | Precision instruments, small machines |
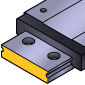 |
Wide Rail | Broader design for higher load capacity and stability | Robotics, automation, heavy load positioning systems |







