
Linear Shafts in Motion Systems: Types, Material
Publish Date: 6 Oct 2025
In the world of manufacturing and industrial automation, smooth and accurate movement is paramount. At the heart of many precision machines, from 3D printers to sophisticated robotics, lies a critical component: the Linear Shaft.
If your application requires linear (straight-line) motion, understanding this fundamental part is essential. MISUMI India, a leading supplier of components, offers a diverse range of Linear Shafts to meet these exact needs.
What is a Linear Shaft?
A Linear Shaft, also commonly known as a Guide Shaft or Slide Shaft, is a straight, precision-machined rod designed to guide a linear bearing (like a ball bushing) and enable low-friction movement along its length.
It essentially serves as the inner raceway for the linear bearing system, ensuring that any load moves along a precise, straight path. High-quality linear shafts are characterized by:
- Precision & Straightness: Minimal deviation from specifications for accurate positioning.
- Hardness: A hardened surface to prevent wear and ensure long life when paired with ball bearings.
- Smooth Surface Finish: Essential for low friction and optimal performance.
When electric current passes through the coils, it interacts with the magnetic field to produce force in a linear direction. The absence of belts, gears, and screws reduces friction, minimizes backlash, and ensures highly efficient and precise movement.
Understanding Linear Shaft Types and Customization
Linear shafts are highly customizable to fit various mechanical requirements. Here are the key classifications and machining options that define the right shaft for your application:
1. Basic Shape Types
The structural foundation of the shaft dictates its function and weight characteristics:
| Solid | Hollow | One End Stepped / Both Ends Stepped | Hollow - One End Stepped / Both Ends Stepped |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
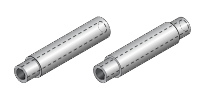 |
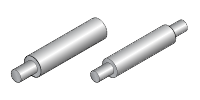
| The most common and robust type, offering maximum rigidity and load capacity. | Significantly lighter than a solid shaft, ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial. The bore can also be used to pass wires, air, or lubrication lines. | Features a change in diameter at one or both ends. This allows for a more secure fit with mounting components like shaft holders or bearings. | Combines the benefits of reduced weight with tailored end support for mounting. |
2. Material Selection: Strength and Environment
Choosing the right material is vital for performance and longevity, especially in challenging environments:
| Material | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| SUJ2 / S45C / Steel | High strength, excellent wear resistance (often induction hardened). Most common choice. | General industrial machinery, high-load systems. |
| Stainless Steel (SUS) | Excellent corrosion resistance in moist or chemical environments. | Food processing, medical equipment, clean rooms, wash-down areas. |
MISUMI India also offers products with a Clean Washed characteristic, perfect for sensitive environments like clean rooms or certain medical applications where contamination must be minimized.
3. End Shape Machining: Connecting Your System
The ends of the linear shaft are often precisely machined to integrate with the rest of the assembly. MISUMI India provides a comprehensive range of end shapes for both the Left and Right sides, offering maximum design flexibility:
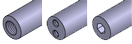 |
Tapped / Tapped Hole / Hex Socket: | Features internal threading for easy bolt-in mounting. |
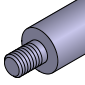 |
Threaded: | Features external threading for use with nuts or mounting into a tapped hole. |
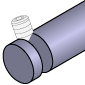 |
Set Screw Grooved: | A flat groove for a set screw to lock the shaft in place, preventing rotation or axial movement. |
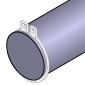 |
With Retaining Ring Grooves: | Used to securely locate and retain components on the shaft using a retaining ring (circlip). |
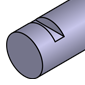 |
Keyway: | A slot to fit a key, primarily used to transmit torque or prevent rotation. |
 |
Tapered: | A gradually reducing diameter, often used for precise self-centering fits. |
 |
No Machining: | A simple, cut-off end, typically used when the shaft is fully supported or when end features are not required. |
Why Choose MISUMI India for Your Linear Shaft Needs?
For engineers and designers in India, specifying high-quality components is made simple with MISUMI. MISUMI India offers an unparalleled selection of linear shafts with a high degree of configurability.
Instead of adapting your design to a limited catalog, MISUMI allows you to define the exact length, diameter, material, and end-machining features you need—virtually creating a custom shaft with standard lead times.
Key Advantages:
- Customizable Ends: Choose from an extensive menu of end shapes (Tapped, Threaded, Set Screw Grooved, etc.) for both the left and right sides.
- Material Diversity: Select the ideal material (SUJ2, S45C, Steel, Stainless Steel) for your load and environment.
- Global Quality, Local Support: Benefit from MISUMI's renowned global quality standards with efficient supply and support right here in India.
Whether you are designing a high-speed packaging machine or a laboratory testing rig, the precision linear shafts from MISUMI India provide the foundation for reliable and accurate linear motion. Explore the configurable options today to achieve the perfect fit for your next project.







