
Exploring Single Axis Robots: Types, Drive Methods, and Specifications
Publish Date: 6 Oct 2025
Single Axis Robots are precision-engineered automation systems designed to provide seamless motion control along a single linear axis. These robots excel in delivering high-speed, accurate, and reliable movement tailored to streamline various industrial processes. They find extensive use in pick-and-place tasks, assembly operations, and material handling applications, offering manufacturers unmatched efficiency and flexibility.
Constructed using robust materials and advanced components such as precision linear guides and ball screws, these robots guarantee smooth and precise motion control. Their design ensures consistent performance even in challenging environments, making them a vital asset in modern automation setups. With options spanning slider types, rod types, and rotary shafts, Single Axis Robots can adapt to diverse operational needs.
Types of Single Axis Robots
Single Axis Robots offer versatile solutions for linear motion along a single axis, suitable for diverse industrial automation needs. Their designs emphasize precision, speed, and load handling to optimize repetitive tasks while saving floor space and installation effort.
Slider Type
Slider type robots provide smooth linear motion using a sliding guide and ball screw or belt drives. They handle loads horizontally up to 80 kg and vertically up to 50 kg, with stroke lengths ranging from 20 mm to 1100 mm. This type is widely used in pick-and-place, assembly, and material handling applications where moderate payload and long stroke are required.
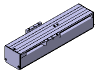
Key features:
- Compact and lightweight design
- High positioning accuracy
- Suitable for medium to large strokes
Rod Type
Rod style robots use rod or piston-like actuators for precise positioning in compact spaces. Driven by ball screws or belts, these units excel in tight environments such as medical equipment or semiconductor handling. They sustain loads similar to sliders but are chosen mainly for their small footprint and smooth motion control.
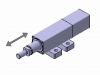
Advantages:
- Space-saving design
- High repeatability
- Flexible mounting options
Rotary Shaft Type
Rotary shaft robots convert rotary motion into linear movement using gears or rack and pinion systems. Their robust construction suits heavy loads and long-travel applications common in automotive and heavy manufacturing. These robots offer high torque but usually operate at lower speeds comparatively.

Benefits:
- Handles heavy-duty loads
- Long stroke capabilities
- Robust and durable system
Key Specifications of Single Axis Robots
| Parameter | Range/Details |
|---|---|
| Types | Slider, Rod, Rotary Shaft |
| Stroke (mm) | 20 to 1100 |
| Max Transportable Mass (Horizontal) (kg) | 1 to 80 |
| Max Transportable Mass (Vertical) (kg) | 0.4 to 50 |
| Maximum Velocity (mm/sec) | 20 to 1800 |
| Drive Methods | Rolled Ball Screw, Ground Ball Screw, Belt, Gear, Rack and Pinion |
Types of Drive Methods
| Drive Method | Description | Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rolled Ball Screw | Uses a ball screw manufactured by rolling process for medium precision motion control. | Cost-effective, smooth motion, moderate precision | General transport, medium load applications |
| Ground Ball Screw | Uses a ball screw ground to precise dimensions for high accuracy and stiffness. | High precision, excellent repeatability, capable of heavy loads | CNC machining, semiconductor manufacturing |
| Belt Drive | Motion driven by a belt and pulley system. | High speed, low noise, flexible stroke length | Light to medium loads, high-speed pick-and-place tasks |
| Gear Drive | Uses gearing mechanisms to translate rotary motion to linear movement. | Suitable for heavy loads, robust operation | Heavy-duty applications requiring torque amplification |
| Rack and Pinion | Linear motion created by rotation of a pinion engaging with a linear rack. | Suitable for long stroke and heavy load transfer, simple design | Large stroke length, heavy-duty transport systems |







