
Ball Screws: What They Are, Types, Materials, and Specifications
Publish Date: 6 Oct 2025
Ball screws are crucial mechanical components designed to deliver precise linear motion in a wide range of industrial and engineering applications. They work on the principle of linear motion rolling bearings, converting rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa, with significantly lower friction compared to traditional lead screws. This efficiency makes them essential where accuracy, repeatability, and smooth operation are critical.
What is Ball Screw
A ball screw consists of a threaded screw shaft and a nut containing recirculating ball bearings that roll along helical grooves. Unlike conventional screws relying on sliding motion, the rolling ball bearings reduce energy loss and friction, achieving efficiencies often exceeding 90%. This results in smoother movement, longer service life, less heat generation, and lower power consumption.
The rolling balls circulate continuously within the nut, maintaining smooth, precise linear motion without backlash or "wiggle." Ball screws are widely used in applications requiring accurate positioning and transportation such as CNC machines, robotics, semiconductor equipment, aerospace systems, and medical devices.
Types of Ball Screws and Components
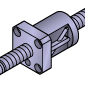 |
Precision Ball Screws | Manufactured to tight tolerances, ideal for high-precision applications like CNC machining, robotics, and semiconductor equipment. |
 |
Rolled Ball Screws | Manufactured using a rolling process, offering cost-effectiveness and suitable for general transport or positioning applications. |
 |
Ball Screw Related Products | Includes accessories such as support bearings, nuts, and housings to complement screw assemblies. |
Key Specifications
| Specification | Range/Details |
|---|---|
| Screw Shaft O.D. | 4 mm to 50 mm |
| Lead (Pitch) | 1 mm to 100 mm |
| Accuracy Grade | C3, C5, C7, C10 |
- C3: Ultra-precision for demanding machining.
- C5: General precision use.
- C7/C10: Cost-efficient for standard positioning or transportation.
Flange Shape Details
Ball screws come with varied flange styles for versatile mounting and usage:
| Flange Shape | Description | Typical Applications | Features & Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
 Square Shape |
Nut with a square flange for mounting | General industrial machinery | Provides stable mounting and easy alignment |
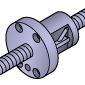 Round Shape |
Nut with a circular flange | Compact machinery, robotics | Saves space, easy to rotate, versatile mounting options |
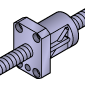 Round, 2 Sides Cut Flat |
Circular flange with two flat cut sides | Applications needing anti-rotation | Helps prevent nut rotation during installation |
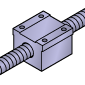 Block Shape |
Rectangular block flange nut | Heavy-duty or large machinery | High rigidity and strength, suitable for large loads |
 Miniature |
Small flange shape for compact or miniature systems | Precision instruments, robotics | Suitable for space-constrained assemblies |
Materials and Compliance
Ball screws are typically produced from alloy steel or stainless steel, often with surface treatments for greater strength and wear resistance. Additionally, they are RoHS compliant (10 substances), ensuring eco-friendly design suitable for industries prioritizing environmental responsibility.







