(!)NOTE : Windows 7 users won’t be able to use some latest features of eCatalog/WOS since Microsoft is ending support for Windows 7 on 14 Jan, 2020. Please upgrade your system for uninterrupted services.
- Please note that the MISUMI Pune office and warehouse will be closed on November 20th due to the state election.
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More information.
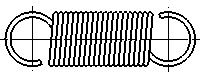
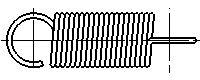
Tension Springs(Material:Titanium Alloy)
Tension springs are springs used for applications that receive a tensile load. Close-wound springs are the standard type since they save space and make effective use of initial tension. Tension springs have a load-receiving hook on both ends. Some models designed for specific applications have plates with holes in them instead of hooks. Tension springs are typically made of materials such as hard drawn steel wire, spring steel, piano wire and stainless steel wire. Different materials are recommended for each tension spring application, so the application and operating environment should be considered when choosing the spring material. For example, general-purpose springs are made from materials such as hard drawn steel wire and piano wire, while heat-resistant springs are made from materials such as stainless steel wire.
Brand |
|
|---|---|
| CAD |
|
| Days to Ship |
|
1 items
- Sort By
-
You can add up to 6 items per a category to the compare list.

SAMINI
Lightweight (a specific gravity of 4.67, half that of steel) and highly corrosion resistant (superior to stainless steel).
[Features]
· Non-magnetic.Free Length Lf(mm) Coil Outer Dia. OD(Ø) Allowable Load (Configurable Range)(N) Wire Dia. d(Ø) Material Length L2 at Allowable Load(mm) Hook Opposing Angle Spring Constant k(N/mm) Type Allowable Load P2(N) Initial Tension Pi(N) Total Number of Winding N Max. Deflection(mm) 50 16 60.01~110.00 2 Titanium Alloy - 180° (Standard) 1.9 Standard Type 80 - 11.5 - From: ₹ 5,303.04 Days to Ship: 5 Day(s) or more  5 Day(s) or more
5 Day(s) or more
| Brand |
|---|
| Product Series |
| From |
| Days to Ship |
| Free Length Lf(mm) |
| Coil Outer Dia. OD(Ø) |
| Allowable Load (Configurable Range)(N) |
| Wire Dia. d(Ø) |
| Material |
| Length L2 at Allowable Load(mm) |
| Hook Opposing Angle |
| Spring Constant k(N/mm) |
| Type |
| Allowable Load P2(N) |
| Initial Tension Pi(N) |
| Total Number of Winding N |
| Max. Deflection(mm) |
You can add up to 6 items per a category to the compare list. | |
| Brand | SAMINI |
| Product Series | |
| From | ₹ 5,303.04 |
| Days to Ship | 5 Day(s) or more |
| Free Length Lf(mm) | 50 |
| Coil Outer Dia. OD(Ø) | 16 |
| Allowable Load (Configurable Range)(N) | 60.01~110.00 |
| Wire Dia. d(Ø) | 2 |
| Material | Titanium Alloy |
| Length L2 at Allowable Load(mm) | - |
| Hook Opposing Angle | 180° (Standard) |
| Spring Constant k(N/mm) | 1.9 |
| Type | Standard Type |
| Allowable Load P2(N) | 80 |
| Initial Tension Pi(N) | - |
| Total Number of Winding N | 11.5 |
| Max. Deflection(mm) | - |
Loading...
Configure
Specification/Dimensions
-
Free Length Lf(mm)
- 2.7
- 2.9
- 3.1
- 3.2
- 3.3
- 3.5
- 3.6
- 3.7
- 3.9
- 4
- 4.1
- 4.3
- 4.4
- 4.5
- 4.6
- 4.8
- 4.9
- 5
- 5.2
- 5.4
- 5.5
- 5.6
- 5.7
- 5.8
- 5.9
- 6
- 6.2
- 6.3
- 6.4
- 6.5
- 6.6
- 6.7
- 6.8
- 7
- 7.1
- 7.2
- 7.3
- 7.4
- 7.5
- 7.7
- 7.8
- 7.9
- 8
- 8.1
- 8.2
- 8.3
- 8.4
- 8.5
- 8.6
- 8.7
- 8.9
- 9
- 9.1
- 9.2
- 9.3
- 9.4
- 9.5
- 9.6
- 9.7
- 9.8
- 10
- 10.1
- 10.2
- 10.3
- 10.4
- 10.5
- 10.6
- 10.7
- 10.8
- 10.9
- 11
- 11.1
- 11.2
- 11.3
- 11.5
- 11.6
- 11.7
- 11.8
- 11.9
- 12
- 12.1
- 12.3
- 12.4
- 12.5
- 12.6
- 12.7
- 12.8
- 12.9
- 13
- 13.1
- 13.2
- 13.3
- 13.4
- 13.5
- 13.6
- 13.7
- 13.8
- 13.9
- 14
- 14.1
- 14.2
- 14.3
- 14.4
- 14.5
- 14.6
- 14.7
- 14.8
- 14.9
- 15
- 15.1
- 15.2
- 15.3
- 15.4
- 15.5
- 15.6
- 15.8
- 15.9
- 16
- 16.1
- 16.2
- 16.3
- 16.4
- 16.5
- 16.6
- 16.7
- 16.8
- 16.9
- 17
- 17.1
- 17.2
- 17.3
- 17.4
- 17.5
- 17.6
- 17.7
- 17.8
- 17.9
- 18
- 18.1
- 18.2
- 18.3
- 18.4
- 18.5
- 18.6
- 18.7
- 18.8
- 18.9
- 19
- 19.1
- 19.2
- 19.3
- 19.4
- 19.5
- 19.6
- 19.7
- 19.8
- 19.9
- 20
- 20.1
- 20.2
- 20.3
- 20.4
- 20.5
- 20.6
- 20.7
- 20.8
- 20.9
- 21
- 21.1
- 21.3
- 21.4
- 21.6
- 21.7
- 21.8
- 22
- 22.1
- 22.2
- 22.3
- 22.4
- 22.5
- 22.6
- 22.7
- 22.8
- 22.9
- 23
- 23.1
- 23.2
- 23.4
- 23.5
- 23.6
- 23.7
- 23.9
- 24
- 24.1
- 24.2
- 24.3
- 24.4
- 24.5
- 24.6
- 24.7
- 24.8
- 24.9
- 25
- 25.1
- 25.2
- 25.3
- 25.4
- 25.5
- 25.6
- 25.9
- 26
- 26.1
- 26.2
- 26.3
- 26.4
- 26.5
- 26.6
- 26.7
- 26.9
- 27
- 27.1
- 27.2
- 27.4
- 27.5
- 27.6
- 27.7
- 27.8
- 27.9
- 28
- 28.1
- 28.2
- 28.3
- 28.4
- 28.5
- 28.6
- 28.7
- 28.9
- 29
- 29.1
- 29.2
- 29.3
- 29.4
- 29.5
- 29.6
- 29.7
- 29.9
- 30
- 30.1
- 30.3
- 30.4
- 30.5
- 30.7
- 30.9
- 31
- 31.1
- 31.2
- 31.3
- 31.4
- 31.5
- 31.7
- 31.8
- 31.9
- 32
- 32.1
- 32.2
- 32.3
- 32.4
- 32.5
- 32.6
- 32.7
- 32.9
- 33
- 33.1
- 33.3
- 33.4
- 33.6
- 33.7
- 33.8
- 34
- 34.3
- 34.5
- 34.6
- 34.7
- 34.9
- 35
- 35.1
- 35.2
- 35.3
- 35.4
- 35.5
- 35.6
- 35.7
- 35.8
- 35.9
- 36
- 36.1
- 36.2
- 36.3
- 36.5
- 36.6
- 36.7
- 36.8
- 36.9
- 37
- 37.2
- 37.3
- 37.4
- 37.5
- 37.6
- 37.7
- 38
- 38.1
- 38.2
- 38.3
- 38.4
- 38.5
- 38.7
- 38.8
- 38.9
- 39
- 39.1
- 39.2
- 39.3
- 39.4
- 39.5
- 39.6
- 39.8
- 40
- 40.1
- 40.3
- 40.5
- 40.6
- 40.7
- 40.9
- 41
- 41.1
- 41.3
- 41.4
- 41.6
- 41.7
- 41.8
- 42
- 42.3
- 42.4
- 42.5
- 42.7
- 42.9
- 43
- 43.4
- 43.5
- 43.6
- 43.9
- 44
- 44.2
- 44.4
- 44.5
- 44.6
- 44.7
- 44.9
- 45
- 45.1
- 45.3
- 45.6
- 45.7
- 45.8
- 46
- 46.1
- 46.2
- 46.4
- 46.5
- 46.7
- 46.8
- 46.9
- 47
- 47.3
- 47.4
- 47.9
- 48
- 48.2
- 48.3
- 48.4
- 48.6
- 49
- 49.3
- 49.5
- 49.6
- 49.7
- 50
- 50.1
- 50.2
- 50.4
- 50.5
- 50.6
- 50.7
- 50.8
- 50.9
- 51
- 51.1
- 51.3
- 51.5
- 51.7
- 52
- 52.1
- 52.2
- 52.3
- 52.4
- 52.5
- 52.6
- 52.8
- 53
- 53.1
- 53.3
- 53.4
- 53.7
- 53.8
- 54
- 54.9
- 55
- 55.2
- 55.4
- 55.5
- 55.7
- 55.9
- 56
- 56.1
- 56.2
- 56.4
- 56.6
- 56.8
- 56.9
- 57
- 57.4
- 57.5
- 57.7
- 57.8
- 58.1
- 58.4
- 58.6
- 58.7
- 58.9
- 59
- 59.1
- 59.3
- 59.4
- 59.8
- 59.9
- 60
- 60.1
- 60.2
- 60.3
- 60.5
- 60.6
- 61
- 61.1
- 61.3
- 61.7
- 62.1
- 62.2
- 62.3
- 62.6
- 62.9
- 63
- 63.1
- 63.2
- 63.4
- 63.5
- 63.6
- 63.8
- 64
- 64.1
- 64.3
- 64.5
- 64.6
- 64.7
- 64.8
- 65
- 65.3
- 65.4
- 65.5
- 65.8
- 65.9
- 66
- 66.1
- 66.6
- 66.9
- 67
- 67.2
- 68
- 68.2
- 68.6
- 69
- 69.3
- 69.4
- 69.9
- 70
- 70.3
- 70.5
- 70.8
- 70.9
- 71
- 71.4
- 71.8
- 72.2
- 72.3
- 72.5
- 72.6
- 73
- 73.1
- 73.2
- 73.3
- 73.6
- 73.8
- 73.9
- 74
- 74.1
- 74.2
- 75
- 75.2
- 75.4
- 75.8
- 76
- 76.1
- 76.5
- 76.7
- 77
- 77.4
- 77.6
- 77.8
- 78
- 78.2
- 78.3
- 78.4
- 78.5
- 78.9
- 79
- 79.7
- 80
- 80.2
- 80.5
- 80.6
- 80.7
- 80.9
- 81
- 81.3
- 81.8
- 82
- 82.4
- 82.6
- 82.8
- 83
- 83.1
- 83.2
- 83.3
- 83.6
- 83.7
- 84.6
- 85
- 85.3
- 85.7
- 86
- 86.2
- 86.6
- 87
- 87.2
- 87.9
- 88.1
- 88.8
- 89.3
- 89.7
- 90
- 90.2
- 90.5
- 90.6
- 90.7
- 91.4
- 91.6
- 92
- 92.2
- 92.5
- 92.9
- 93
- 93.4
- 93.6
- 94.2
- 94.6
- 94.9
- 95
- 95.6
- 95.8
- 95.9
- 96.5
- 97
- 98.6
- 98.7
- 99
- 99.3
- 100
- 100.2
- 100.3
- 100.7
- 101
- 101.6
- 101.8
- 102
- 102.2
- 103.2
- 104
- 104.1
- 104.6
- 104.7
- 104.8
- 105
- 105.3
- 105.8
- 106
- 106.1
- 106.6
- 107
- 107.4
- 109
- 110
- 110.9
- 111
- 111.7
- 111.8
- 112.5
- 113.2
- 115
- 115.5
- 115.6
- 115.7
- 116
- 116.1
- 116.2
- 117
- 117.4
- 117.9
- 118
- 118.6
- 119.7
- 120
- 120.1
- 120.6
- 121.3
- 121.8
- 122
- 122.1
- 123.2
- 124.1
- 125
- 125.4
- 125.6
- 126.2
- 128.6
- 130
- 130.7
- 130.9
- 131.6
- 131.8
- 133.1
- 133.3
- 138
- 138.6
- 139
- 139.7
- 140
- 140.6
- 141.6
- 142
- 142.1
- 142.9
- 144.6
- 145
- 146
- 146.1
- 147
- 147.3
- 148.2
- 150
- 150.1
- 150.4
- 150.7
- 151.6
- 152.8
- 153
- 153.4
- 155.9
- 157.8
- 160.5
- 161
- 162
- 162.2
- 164.7
- 166.1
- 166.6
- 169.3
- 175
- 175.7
- 177.6
- 178.6
- 179
- 180.7
- 184.1
- 188.4
- 191.1
- 191.8
- 197.2
- 200
- 200.6
- 202
- 208.2
- 211.6
- 223.2
- 223.6
- 230.9
- 235
- 239.7
- 250.7
- 260
- 266.1
- 280
- 288
- 295
- 300
- 316
- 336
- 341
- 354
- 355
- 363
- 376
- 416
- 431
- 436
- 438
- 454
- 476
- 500
- 521
- 1000
-
Coil Outer Dia. OD(Ø)
- 0.9
- 1.1
- 1.12
- 1.3
- 1.32
- 1.36
- 1.4
- 1.72
- 1.76
- 1.8
- 1.85
- 1.92
- 2
- 2.16
- 2.2
- 2.25
- 2.3
- 2.32
- 2.4
- 2.5
- 2.6
- 2.7
- 2.75
- 2.82
- 2.9
- 3
- 3.2
- 3.45
- 3.5
- 3.52
- 3.6
- 3.7
- 3.83
- 4
- 4.32
- 4.4
- 4.5
- 4.63
- 4.8
- 5
- 5.4
- 5.5
- 5.63
- 5.8
- 6
- 6.3
- 6.8
- 6.93
- 7
- 7.1
- 7.3
- 7.55
- 8
- 8.63
- 8.8
- 9
- 9.25
- 9.6
- 10
- 10.5
- 10.8
- 11
- 11.25
- 11.5
- 11.6
- 12
- 12.5
- 13
- 13.2
- 13.5
- 13.75
- 14
- 14.1
- 14.5
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 17.25
- 17.6
- 18
- 18.5
- 20
- 21.6
- 22
- 22.5
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 27.5
- 28
- 30
- 32
- 34.5
- 35
- 40
- 48
- 50
- 65
- 75
- 85
- 100
-
Allowable Load (Configurable Range)(N)
- ~1.25
- 1.26~3.50
- 3.51~8.00
- 8.01~15.00
- 15.01~30.00
- 30.01~60.00
- 60.01~110.00
- 110.01~
-
Wire Dia. d(Ø)
-
Material
- Stainless Steel Wire
- Piano Wire
- Titanium Alloy
- Hard Steel Wire
- SWP-B
-
Length L2 at Allowable Load(mm)
- 3.7
- 4.1
- 4.6
- 4.7
- 4.8
- 4.9
- 5.0
- 5.2
- 5.3
- 5.4
- 5.5
- 5.7
- 5.8
- 5.9
- 6.0
- 6.1
- 6.2
- 6.3
- 6.5
- 6.6
- 6.8
- 6.9
- 7
- 7.1
- 7.2
- 7.3
- 7.4
- 7.5
- 7.9
- 8
- 8.1
- 8.2
- 8.3
- 8.4
- 8.5
- 8.6
- 8.7
- 8.8
- 9
- 9.1
- 9.2
- 9.4
- 9.5
- 9.6
- 9.7
- 9.8
- 9.9
- 10
- 10.1
- 10.2
- 10.3
- 10.4
- 10.5
- 10.6
- 10.8
- 10.9
- 11
- 11.1
- 11.2
- 11.3
- 11.4
- 11.5
- 11.6
- 11.7
- 11.8
- 11.9
- 12
- 12.1
- 12.2
- 12.3
- 12.4
- 12.5
- 12.6
- 12.7
- 12.8
- 12.9
- 13
- 13.1
- 13.3
- 13.4
- 13.5
- 13.6
- 13.7
- 13.8
- 14
- 14.1
- 14.2
- 14.3
- 14.4
- 14.5
- 14.6
- 14.8
- 14.9
- 15
- 15.1
- 15.2
- 15.3
- 15.4
- 15.5
- 15.6
- 15.7
- 15.9
- 16
- 16.1
- 16.3
- 16.4
- 16.5
- 16.6
- 16.7
- 16.8
- 16.9
- 17
- 17.1
- 17.2
- 17.4
- 17.5
- 17.7
- 17.8
- 17.9
- 18.1
- 18.2
- 18.3
- 18.4
- 18.5
- 18.6
- 18.7
- 18.8
- 18.9
- 19
- 19.1
- 19.2
- 19.3
- 19.4
- 19.5
- 19.6
- 19.7
- 19.8
- 19.9
- 20.1
- 20.2
- 20.3
- 20.4
- 20.5
- 20.6
- 20.7
- 20.8
- 20.9
- 21
- 21.1
- 21.2
- 21.3
- 21.4
- 21.5
- 21.6
- 21.7
- 21.8
- 21.9
- 22.1
- 22.2
- 22.3
- 22.4
- 22.5
- 22.6
- 22.7
- 22.8
- 22.9
- 23.0
- 23.1
- 23.2
- 23.4
- 23.5
- 23.6
- 23.7
- 23.8
- 23.9
- 24
- 24.1
- 24.3
- 24.4
- 24.5
- 24.6
- 24.7
- 24.8
- 25
- 25.1
- 25.2
- 25.3
- 25.4
- 25.5
- 25.6
- 25.7
- 25.8
- 25.9
- 26
- 26.1
- 26.2
- 26.4
- 26.5
- 26.6
- 26.7
- 26.8
- 26.9
- 27
- 27.1
- 27.2
- 27.3
- 27.5
- 27.6
- 28
- 28.1
- 28.2
- 28.3
- 28.5
- 28.6
- 28.7
- 28.9
- 29
- 29.2
- 29.3
- 29.4
- 29.5
- 29.6
- 29.7
- 29.8
- 29.9
- 30
- 30.1
- 30.2
- 30.3
- 30.4
- 30.5
- 30.6
- 30.7
- 30.8
- 30.9
- 31
- 31.1
- 31.2
- 31.3
- 31.4
- 31.6
- 31.7
- 31.8
- 32
- 32.1
- 32.2
- 32.3
- 32.4
- 32.5
- 32.6
- 32.7
- 32.8
- 32.9
- 33
- 33.1
- 33.3
- 33.4
- 33.5
- 33.6
- 33.7
- 33.8
- 33.9
- 34
- 34.1
- 34.2
- 34.3
- 34.4
- 34.5
- 34.6
- 34.7
- 34.8
- 34.9
- 35
- 35.2
- 35.4
- 35.5
- 35.6
- 35.7
- 35.8
- 35.9
- 36.1
- 36.2
- 36.4
- 36.5
- 36.6
- 36.7
- 36.8
- 36.9
- 37
- 37.1
- 37.2
- 37.3
- 37.4
- 37.5
- 37.6
- 37.7
- 37.8
- 37.9
- 38
- 38.1
- 38.2
- 38.3
- 38.4
- 38.5
- 38.6
- 38.7
- 38.8
- 38.9
- 39
- 39.2
- 39.4
- 39.5
- 39.6
- 39.7
- 39.8
- 39.9
- 40
- 40.1
- 40.3
- 40.4
- 40.5
- 40.7
- 40.9
- 41
- 41.1
- 41.2
- 41.3
- 41.4
- 41.5
- 41.6
- 41.7
- 41.8
- 41.9
- 42
- 42.1
- 42.3
- 42.4
- 42.5
- 42.6
- 42.7
- 42.8
- 42.9
- 43.1
- 43.2
- 43.3
- 43.4
- 43.5
- 43.7
- 43.8
- 43.9
- 44.1
- 44.2
- 44.3
- 44.4
- 44.5
- 44.7
- 44.8
- 44.9
- 45
- 45.2
- 45.4
- 45.5
- 45.6
- 45.7
- 45.8
- 45.9
- 46.0
- 46.1
- 46.2
- 46.3
- 46.5
- 46.6
- 46.7
- 46.8
- 47
- 47.1
- 47.2
- 47.3
- 47.4
- 47.5
- 47.6
- 47.7
- 47.8
- 48
- 48.1
- 48.2
- 48.3
- 48.4
- 48.5
- 48.6
- 48.7
- 48.9
- 49
- 49.1
- 49.2
- 49.4
- 49.5
- 49.6
- 49.9
- 50
- 50.1
- 50.2
- 50.3
- 50.4
- 50.5
- 50.6
- 50.7
- 50.8
- 50.9
- 51
- 51.2
- 51.4
- 51.5
- 51.6
- 51.7
- 51.8
- 51.9
- 52
- 52.1
- 52.2
- 52.3
- 52.4
- 52.5
- 52.6
- 52.7
- 52.8
- 53.0
- 53.2
- 53.4
- 53.5
- 53.7
- 53.8
- 53.9
- 54
- 54.3
- 54.4
- 54.6
- 54.8
- 54.9
- 55
- 55.1
- 55.2
- 55.3
- 55.4
- 55.5
- 55.7
- 55.8
- 55.9
- 56.2
- 56.3
- 56.4
- 56.5
- 56.6
- 56.7
- 56.8
- 56.9
- 57
- 57.1
- 57.2
- 57.3
- 57.4
- 57.5
- 57.6
- 57.7
- 57.8
- 57.9
- 58
- 58.1
- 58.2
- 58.3
- 58.4
- 58.5
- 58.6
- 58.7
- 58.8
- 58.9
- 59.0
- 59.1
- 59.2
- 59.3
- 59.4
- 59.6
- 59.8
- 59.9
- 60
- 60.1
- 60.3
- 60.6
- 60.7
- 60.8
- 60.9
- 61
- 61.1
- 61.2
- 61.3
- 61.4
- 61.5
- 61.6
- 61.7
- 62.2
- 62.3
- 62.5
- 62.7
- 62.8
- 62.9
- 63
- 63.2
- 63.3
- 63.5
- 63.6
- 63.7
- 63.8
- 63.9
- 64
- 64.2
- 64.4
- 64.5
- 64.6
- 64.7
- 65
- 65.1
- 65.2
- 65.3
- 65.4
- 65.5
- 65.6
- 65.7
- 65.9
- 66
- 66.2
- 66.3
- 66.4
- 66.5
- 66.6
- 66.7
- 66.8
- 66.9
- 67
- 67.1
- 67.2
- 67.3
- 67.5
- 67.6
- 67.7
- 67.8
- 68
- 68.1
- 68.2
- 68.3
- 68.4
- 68.5
- 68.6
- 68.7
- 68.9
- 69.0
- 69.2
- 69.3
- 69.6
- 69.7
- 70
- 70.1
- 70.2
- 70.3
- 70.4
- 70.5
- 70.6
- 70.9
- 71
- 71.2
- 71.3
- 71.4
- 71.5
- 71.6
- 71.7
- 71.8
- 71.9
- 72.0
- 72.1
- 72.2
- 72.3
- 72.4
- 72.6
- 72.7
- 72.8
- 72.9
- 73
- 73.1
- 73.2
- 73.3
- 73.4
- 73.5
- 73.7
- 73.8
- 73.9
- 74
- 74.1
- 74.2
- 74.3
- 74.5
- 74.6
- 74.7
- 74.8
- 74.9
- 75
- 75.1
- 75.2
- 75.3
- 75.4
- 75.6
- 75.7
- 75.9
- 76
- 76.1
- 76.3
- 76.4
- 76.5
- 76.6
- 76.7
- 76.9
- 77
- 77.1
- 77.2
- 77.3
- 77.5
- 77.6
- 77.7
- 77.9
- 78.0
- 78.1
- 78.2
- 78.4
- 78.5
- 78.6
- 78.7
- 78.8
- 79.1
- 79.2
- 79.4
- 79.5
- 79.6
- 79.7
- 79.8
- 80
- 80.1
- 80.2
- 80.3
- 80.5
- 80.6
- 80.7
- 81
- 81.1
- 81.2
- 81.3
- 81.4
- 81.6
- 81.8
- 81.9
- 82
- 82.2
- 82.3
- 82.5
- 82.6
- 82.7
- 83
- 83.1
- 83.2
- 83.3
- 83.4
- 83.6
- 83.7
- 83.8
- 84
- 84.2
- 84.3
- 84.4
- 84.5
- 84.6
- 84.7
- 84.9
- 85
- 85.1
- 85.2
- 85.3
- 85.6
- 85.8
- 86
- 86.2
- 86.4
- 86.5
- 86.6
- 86.7
- 86.8
- 86.9
- 87.2
- 87.4
- 87.5
- 87.7
- 87.8
- 87.9
- 88.2
- 88.3
- 88.4
- 88.5
- 88.6
- 88.7
- 89.0
- 89.1
- 89.2
- 89.3
- 89.4
- 89.5
- 89.6
- 89.7
- 89.9
- 90
- 90.2
- 90.3
- 90.4
- 90.5
- 90.6
- 90.7
- 90.8
- 90.9
- 91
- 91.1
- 91.3
- 91.4
- 91.5
- 91.6
- 91.7
- 91.8
- 91.9
- 92
- 92.2
- 92.4
- 92.5
- 92.6
- 92.7
- 92.8
- 92.9
- 93.1
- 93.2
- 93.3
- 93.5
- 93.7
- 94.3
- 94.5
- 94.6
- 94.7
- 94.8
- 95
- 95.1
- 95.2
- 95.3
- 95.4
- 95.5
- 95.6
- 95.7
- 95.8
- 95.9
- 96
- 96.2
- 96.4
- 96.5
- 96.6
- 96.7
- 96.8
- 96.9
- 97
- 97.1
- 97.2
- 97.3
- 97.5
- 97.6
- 97.8
- 97.9
- 98
- 98.1
- 98.2
- 98.8
- 99.0
- 99.1
- 99.2
- 99.3
- 99.4
- 99.5
- 99.7
- 99.8
- 100
- 100.3
- 100.5
- 100.7
- 100.8
- 100.9
- 101
- 101.1
- 101.2
- 101.3
- 101.7
- 101.8
- 102.0
- 102.1
- 102.3
- 102.4
- 102.5
- 103.0
- 103.1
- 103.3
- 103.5
- 103.6
- 103.7
- 103.8
- 104.1
- 104.2
- 104.3
- 104.5
- 104.6
- 104.7
- 104.8
- 104.9
- 105
- 105.2
- 105.6
- 106
- 106.1
- 106.4
- 106.5
- 106.6
- 106.8
- 107.1
- 107.3
- 107.4
- 107.5
- 107.6
- 108.1
- 108.2
- 108.3
- 108.4
- 108.5
- 108.6
- 108.8
- 109
- 109.1
- 109.4
- 109.5
- 110
- 110.3
- 110.5
- 110.6
- 110.8
- 110.9
- 111
- 111.1
- 111.2
- 111.4
- 111.5
- 111.6
- 111.8
- 111.9
- 112
- 112.2
- 112.6
- 112.7
- 112.8
- 112.9
- 113
- 113.1
- 113.3
- 113.6
- 114.1
- 114.2
- 114.3
- 114.4
- 114.5
- 114.8
- 114.9
- 115.0
- 115.2
- 115.3
- 115.5
- 115.6
- 115.8
- 115.9
- 116.0
- 116.1
- 116.2
- 116.3
- 116.4
- 116.7
- 116.8
- 116.9
- 117.6
- 117.8
- 118.1
- 118.3
- 118.4
- 118.5
- 118.6
- 118.7
- 118.8
- 119.0
- 119.3
- 119.4
- 119.6
- 119.7
- 119.9
- 120
- 120.1
- 120.2
- 120.3
- 120.6
- 120.8
- 121
- 121.1
- 121.2
- 121.3
- 121.4
- 121.6
- 121.7
- 121.9
- 122
- 122.1
- 122.3
- 122.4
- 122.9
- 123.1
- 123.2
- 123.3
- 123.4
- 123.5
- 123.6
- 123.8
- 123.9
- 124
- 124.1
- 124.8
- 124.9
- 125
- 125.1
- 125.4
- 126
- 126.1
- 126.3
- 126.5
- 126.6
- 126.8
- 126.9
- 127.0
- 127.1
- 127.2
- 127.5
- 127.7
- 127.8
- 128
- 128.5
- 129
- 129.1
- 129.3
- 129.5
- 129.6
- 129.7
- 129.9
- 130
- 130.1
- 130.2
- 130.3
- 130.5
- 131
- 131.9
- 132.2
- 133
- 133.2
- 133.6
- 133.7
- 133.9
- 134
- 134.1
- 134.2
- 134.3
- 135.0
- 135.3
- 135.7
- 135.8
- 136.1
- 136.2
- 136.7
- 136.9
- 137.2
- 138.1
- 138.2
- 138.3
- 138.4
- 139.1
- 139.4
- 139.5
- 139.6
- 139.7
- 140
- 140.1
- 140.3
- 140.4
- 140.5
- 140.8
- 141
- 141.1
- 141.3
- 141.8
- 141.9
- 142
- 142.3
- 142.6
- 142.7
- 142.8
- 143.1
- 143.6
- 143.8
- 144.1
- 144.4
- 144.5
- 144.8
- 145.2
- 145.3
- 145.4
- 145.5
- 145.6
- 145.8
- 146.2
- 146.7
- 146.8
- 147.4
- 147.5
- 147.9
- 148.4
- 149
- 149.2
- 149.3
- 149.4
- 149.5
- 150.0
- 150.4
- 150.5
- 150.9
- 151.1
- 151.2
- 151.3
- 152.1
- 152.3
- 152.5
- 152.6
- 152.8
- 152.9
- 153
- 153.1
- 153.2
- 153.4
- 154.1
- 154.4
- 154.6
- 154.7
- 154.8
- 154.9
- 155.2
- 155.5
- 156
- 156.4
- 156.5
- 157
- 157.2
- 157.5
- 157.8
- 158.1
- 158.2
- 158.3
- 158.7
- 158.8
- 158.9
- 159
- 159.5
- 160.2
- 160.5
- 160.6
- 161.3
- 161.5
- 162.1
- 162.6
- 162.8
- 163.2
- 163.5
- 164.5
- 165
- 165.2
- 165.4
- 166
- 167.5
- 167.6
- 168.4
- 168.5
- 168.8
- 169.1
- 169.2
- 169.4
- 169.5
- 169.6
- 169.8
- 170.0
- 170.1
- 170.3
- 170.5
- 170.9
- 171.8
- 172.4
- 172.5
- 173.3
- 174.7
- 174.9
- 175
- 175.6
- 175.7
- 175.9
- 176.2
- 176.3
- 176.4
- 176.7
- 176.9
- 177.1
- 178
- 178.2
- 178.3
- 178.5
- 178.6
- 178.8
- 179.3
- 179.4
- 179.5
- 180.2
- 180.5
- 180.8
- 180.9
- 181.1
- 181.3
- 181.6
- 181.7
- 182.8
- 183.3
- 183.8
- 183.9
- 184.2
- 184.4
- 185
- 185.1
- 185.4
- 185.5
- 185.7
- 187.1
- 187.2
- 187.3
- 187.8
- 188.2
- 188.3
- 189.5
- 190.0
- 190.1
- 190.2
- 190.4
- 191.3
- 192.1
- 192.4
- 192.9
- 193.6
- 193.9
- 194.6
- 195.6
- 195.7
- 197.1
- 197.2
- 198.1
- 198.4
- 198.6
- 199.6
- 200.1
- 200.3
- 200.6
- 200.9
- 201.4
- 202.7
- 203.7
- 204.4
- 205.7
- 206
- 206.2
- 206.6
- 206.8
- 207.0
- 207.1
- 208.0
- 208.6
- 209.4
- 209.5
- 209.7
- 210.0
- 211.0
- 212.1
- 213.5
- 213.7
- 214
- 214.2
- 214.8
- 214.9
- 215.6
- 216
- 216.3
- 216.6
- 217.2
- 217.3
- 218.2
- 218.3
- 218.7
- 219.4
- 220.1
- 221.4
- 221.5
- 221.7
- 221.9
- 222.3
- 223.1
- 224.0
- 225.6
- 225.7
- 226.1
- 227
- 227.2
- 227.3
- 227.4
- 227.9
- 228.6
- 229.3
- 229.5
- 229.7
- 230.0
- 230.3
- 230.4
- 231.3
- 232
- 233.3
- 234.8
- 235
- 235.2
- 236.1
- 236.4
- 236.6
- 236.9
- 237.8
- 238.7
- 239.8
- 240.2
- 241.2
- 242
- 243.1
- 244.8
- 247.5
- 248.3
- 248.5
- 250
- 250.5
- 252.0
- 253.3
- 254.9
- 256.2
- 256.6
- 259.4
- 261.5
- 261.6
- 265.1
- 265.4
- 265.5
- 265.6
- 266.4
- 267.5
- 268
- 268.4
- 268.5
- 269.9
- 270.5
- 271.2
- 274.3
- 274.7
- 275.2
- 275.9
- 277.4
- 277.7
- 278.3
- 279
- 279.3
- 281.3
- 282
- 282.8
- 284.0
- 285.1
- 285.5
- 286.9
- 287.6
- 288.8
- 289.5
- 289.9
- 290.5
- 290.6
- 291.9
- 292.1
- 293.2
- 294.6
- 297.6
- 299.3
- 301.4
- 301.5
- 303.0
- 303.1
- 303.4
- 316.6
- 317.9
- 326.9
- 328.4
- 328.5
- 331.3
- 331.7
- 333.0
- 334.7
- 335.2
- 337.0
- 338
- 338.3
- 340.2
- 342.5
- 342.6
- 343.6
- 343.7
- 345.9
- 346.8
- 350
- 352.9
- 353.6
- 353.9
- 355.2
- 357.3
- 360.7
- 365.7
- 367.0
- 370.1
- 381.2
- 402.4
- 404.7
- 406.5
- 406.8
- 412.2
- 416.4
- 416.7
- 418.1
- 422.1
- 425.7
- 428
- 428.2
- 432.0
- 432.2
- 432.6
- 439.1
- 439.4
- 440.5
- 447.0
- 448.3
- 461.1
- 494.2
- 499.7
- 505.1
- 512.3
- 512.9
- 518.4
- 527.3
- 535.3
- 535.9
- 543.9
- 547.0
- 559.0
- 614.3
- 621.6
- 629.5
- 642.0
- 669.2
- 770.3
- 782.9
- 830.6
-
Hook Opposing Angle
-
Spring Constant k(N/mm)
- 0.0019
- 0.002
- 0.0041
- 0.0042
- 0.0058
- 0.0059
- 0.006
- 0.0069
- 0.007
- 0.0073
- 0.0078
- 0.008
- 0.0086
- 0.0088
- 0.009
- 0.0098
- 0.01
- 0.0108
- 0.011
- 0.0116
- 0.0118
- 0.012
- 0.0127
- 0.013
- 0.0134
- 0.0137
- 0.014
- 0.0147
- 0.015
- 0.0157
- 0.016
- 0.0167
- 0.0168
- 0.017
- 0.0176
- 0.018
- 0.0186
- 0.019
- 0.0193
- 0.02
- 0.0206
- 0.021
- 0.0216
- 0.022
- 0.0225
- 0.023
- 0.0232
- 0.0235
- 0.024
- 0.0245
- 0.025
- 0.0255
- 0.026
- 0.0262
- 0.0265
- 0.027
- 0.0274
- 0.028
- 0.0284
- 0.029
- 0.03
- 0.0304
- 0.0306
- 0.031
- 0.0314
- 0.032
- 0.0323
- 0.033
- 0.0337
- 0.034
- 0.0342
- 0.0343
- 0.035
- 0.0353
- 0.036
- 0.0363
- 0.037
- 0.0372
- 0.038
- 0.0382
- 0.039
- 0.0392
- 0.04
- 0.0402
- 0.041
- 0.0412
- 0.042
- 0.0421
- 0.043
- 0.0431
- 0.0433
- 0.044
- 0.0441
- 0.045
- 0.0451
- 0.046
- 0.047
- 0.0471
- 0.048
- 0.049
- 0.05
- 0.051
- 0.0519
- 0.052
- 0.0529
- 0.053
- 0.0535
- 0.0539
- 0.054
- 0.0549
- 0.055
- 0.0559
- 0.056
- 0.0563
- 0.0568
- 0.057
- 0.0578
- 0.058
- 0.0588
- 0.059
- 0.0598
- 0.06
- 0.0608
- 0.061
- 0.0617
- 0.062
- 0.0627
- 0.063
- 0.064
- 0.0647
- 0.065
- 0.0657
- 0.066
- 0.0666
- 0.067
- 0.0676
- 0.068
- 0.0686
- 0.069
- 0.0696
- 0.07
- 0.0706
- 0.0708
- 0.071
- 0.0715
- 0.072
- 0.0725
- 0.073
- 0.0735
- 0.074
- 0.0745
- 0.075
- 0.076
- 0.0764
- 0.077
- 0.078
- 0.0784
- 0.079
- 0.0794
- 0.08
- 0.0804
- 0.081
- 0.0813
- 0.082
- 0.0823
- 0.083
- 0.0833
- 0.084
- 0.0843
- 0.085
- 0.0853
- 0.086
- 0.0862
- 0.087
- 0.0872
- 0.088
- 0.0882
- 0.089
- 0.0892
- 0.09
- 0.0902
- 0.0904
- 0.091
- 0.0911
- 0.092
- 0.093
- 0.0931
- 0.094
- 0.0941
- 0.095
- 0.0951
- 0.096
- 0.097
- 0.098
- 0.099
- 0.1
- 0.1009
- 0.101
- 0.102
- 0.1029
- 0.103
- 0.104
- 0.105
- 0.1058
- 0.106
- 0.1068
- 0.107
- 0.1078
- 0.108
- 0.109
- 0.1098
- 0.11
- 0.1107
- 0.111
- 0.112
- 0.1127
- 0.113
- 0.1137
- 0.114
- 0.1147
- 0.115
- 0.116
- 0.117
- 0.1176
- 0.118
- 0.1186
- 0.119
- 0.12
- 0.121
- 0.122
- 0.123
- 0.1235
- 0.124
- 0.1245
- 0.125
- 0.1254
- 0.126
- 0.127
- 0.1274
- 0.128
- 0.1284
- 0.129
- 0.13
- 0.1303
- 0.131
- 0.132
- 0.1323
- 0.133
- 0.1333
- 0.134
- 0.1343
- 0.135
- 0.136
- 0.137
- 0.1372
- 0.138
- 0.1382
- 0.139
- 0.1392
- 0.14
- 0.1401
- 0.141
- 0.1411
- 0.142
- 0.1421
- 0.143
- 0.144
- 0.145
- 0.146
- 0.147
- 0.148
- 0.149
- 0.1499
- 0.15
- 0.1509
- 0.151
- 0.152
- 0.1539
- 0.154
- 0.1548
- 0.155
- 0.156
- 0.1568
- 0.157
- 0.1578
- 0.158
- 0.1588
- 0.159
- 0.1597
- 0.16
- 0.1607
- 0.161
- 0.162
- 0.163
- 0.1637
- 0.164
- 0.165
- 0.1656
- 0.166
- 0.1666
- 0.167
- 0.1676
- 0.168
- 0.169
- 0.1695
- 0.17
- 0.1705
- 0.171
- 0.1715
- 0.172
- 0.173
- 0.174
- 0.175
- 0.176
- 0.1764
- 0.177
- 0.178
- 0.179
- 0.18
- 0.1803
- 0.181
- 0.182
- 0.183
- 0.184
- 0.185
- 0.1852
- 0.186
- 0.1862
- 0.187
- 0.188
- 0.1882
- 0.19
- 0.191
- 0.192
- 0.194
- 0.195
- 0.196
- 0.197
- 0.198
- 0.1989
- 0.199
- 0.2
- 0.2009
- 0.201
- 0.202
- 0.203
- 0.2038
- 0.204
- 0.205
- 0.2058
- 0.206
- 0.2068
- 0.207
- 0.208
- 0.209
- 0.2097
- 0.21
- 0.211
- 0.2117
- 0.212
- 0.213
- 0.214
- 0.2146
- 0.215
- 0.2156
- 0.216
- 0.2166
- 0.217
- 0.2176
- 0.218
- 0.219
- 0.22
- 0.221
- 0.222
- 0.2225
- 0.223
- 0.2234
- 0.224
- 0.2244
- 0.225
- 0.2254
- 0.226
- 0.228
- 0.229
- 0.23
- 0.231
- 0.233
- 0.2332
- 0.234
- 0.235
- 0.2352
- 0.237
- 0.238
- 0.2381
- 0.239
- 0.24
- 0.2401
- 0.241
- 0.2411
- 0.242
- 0.244
- 0.245
- 0.246
- 0.247
- 0.2479
- 0.248
- 0.2489
- 0.249
- 0.2499
- 0.25
- 0.251
- 0.2519
- 0.252
- 0.253
- 0.2548
- 0.255
- 0.257
- 0.2577
- 0.258
- 0.259
- 0.2597
- 0.26
- 0.261
- 0.262
- 0.263
- 0.264
- 0.2646
- 0.265
- 0.266
- 0.2675
- 0.268
- 0.269
- 0.27
- 0.2705
- 0.271
- 0.272
- 0.273
- 0.274
- 0.2744
- 0.275
- 0.276
- 0.2764
- 0.277
- 0.278
- 0.279
- 0.28
- 0.281
- 0.282
- 0.2822
- 0.283
- 0.284
- 0.2842
- 0.285
- 0.286
- 0.287
- 0.2871
- 0.288
- 0.289
- 0.29
- 0.291
- 0.293
- 0.294
- 0.297
- 0.299
- 0.2999
- 0.3
- 0.3009
- 0.301
- 0.302
- 0.303
- 0.3038
- 0.304
- 0.307
- 0.308
- 0.309
- 0.3097
- 0.31
- 0.3107
- 0.311
- 0.312
- 0.3126
- 0.313
- 0.3136
- 0.314
- 0.3146
- 0.315
- 0.316
- 0.3165
- 0.317
- 0.318
- 0.3195
- 0.32
- 0.3205
- 0.321
- 0.322
- 0.323
- 0.3234
- 0.324
- 0.3244
- 0.325
- 0.3263
- 0.327
- 0.329
- 0.33
- 0.331
- 0.3312
- 0.332
- 0.333
- 0.334
- 0.3342
- 0.335
- 0.3352
- 0.337
- 0.338
- 0.34
- 0.3401
- 0.341
- 0.342
- 0.343
- 0.344
- 0.346
- 0.3469
- 0.347
- 0.348
- 0.349
- 0.35
- 0.3508
- 0.351
- 0.3518
- 0.352
- 0.3528
- 0.353
- 0.354
- 0.355
- 0.3557
- 0.356
- 0.357
- 0.358
- 0.36
- 0.361
- 0.362
- 0.3626
- 0.363
- 0.364
- 0.366
- 0.367
- 0.368
- 0.3685
- 0.369
- 0.37
- 0.372
- 0.3724
- 0.373
- 0.3744
- 0.375
- 0.376
- 0.3773
- 0.378
- 0.38
- 0.381
- 0.382
- 0.3822
- 0.383
- 0.3832
- 0.384
- 0.385
- 0.386
- 0.387
- 0.39
- 0.391
- 0.392
- 0.393
- 0.3969
- 0.397
- 0.3979
- 0.398
- 0.3989
- 0.4
- 0.4018
- 0.402
- 0.404
- 0.4067
- 0.407
- 0.408
- 0.409
- 0.41
- 0.4116
- 0.412
- 0.413
- 0.414
- 0.4145
- 0.415
- 0.416
- 0.417
- 0.418
- 0.4194
- 0.42
- 0.421
- 0.4214
- 0.422
- 0.423
- 0.425
- 0.426
- 0.427
- 0.428
- 0.429
- 0.43
- 0.431
- 0.4312
- 0.432
- 0.434
- 0.435
- 0.436
- 0.437
- 0.439
- 0.44
- 0.441
- 0.442
- 0.4439
- 0.444
- 0.445
- 0.449
- 0.45
- 0.4508
- 0.451
- 0.453
- 0.454
- 0.455
- 0.457
- 0.458
- 0.459
- 0.46
- 0.4606
- 0.461
- 0.464
- 0.465
- 0.4675
- 0.468
- 0.4694
- 0.47
- 0.4704
- 0.471
- 0.474
- 0.476
- 0.477
- 0.4782
- 0.479
- 0.48
- 0.4802
- 0.481
- 0.483
- 0.4831
- 0.485
- 0.486
- 0.487
- 0.489
- 0.49
- 0.491
- 0.4939
- 0.494
- 0.495
- 0.496
- 0.4998
- 0.5
- 0.5027
- 0.503
- 0.504
- 0.5057
- 0.506
- 0.509
- 0.5096
- 0.51
- 0.512
- 0.5125
- 0.513
- 0.514
- 0.515
- 0.518
- 0.519
- 0.5194
- 0.52
- 0.522
- 0.5223
- 0.523
- 0.524
- 0.525
- 0.526
- 0.5272
- 0.528
- 0.529
- 0.5292
- 0.53
- 0.531
- 0.5312
- 0.532
- 0.534
- 0.535
- 0.538
- 0.539
- 0.54
- 0.542
- 0.544
- 0.547
- 0.548
- 0.5488
- 0.549
- 0.55
- 0.551
- 0.552
- 0.553
- 0.554
- 0.555
- 0.5557
- 0.556
- 0.5566
- 0.557
- 0.5586
- 0.559
- 0.56
- 0.561
- 0.564
- 0.565
- 0.566
- 0.567
- 0.5684
- 0.569
- 0.57
- 0.573
- 0.575
- 0.576
- 0.577
- 0.578
- 0.5782
- 0.579
- 0.58
- 0.581
- 0.583
- 0.585
- 0.587
- 0.588
- 0.59
- 0.593
- 0.595
- 0.596
- 0.5978
- 0.598
- 0.599
- 0.6
- 0.602
- 0.604
- 0.6056
- 0.606
- 0.6076
- 0.608
- 0.609
- 0.611
- 0.6174
- 0.618
- 0.62
- 0.621
- 0.623
- 0.625
- 0.6252
- 0.626
- 0.627
- 0.6272
- 0.628
- 0.6282
- 0.629
- 0.63
- 0.631
- 0.632
- 0.6321
- 0.633
- 0.635
- 0.637
- 0.64
- 0.641
- 0.642
- 0.643
- 0.6468
- 0.647
- 0.65
- 0.652
- 0.6527
- 0.653
- 0.6537
- 0.654
- 0.6566
- 0.657
- 0.659
- 0.66
- 0.661
- 0.664
- 0.6664
- 0.667
- 0.668
- 0.669
- 0.67
- 0.676
- 0.678
- 0.68
- 0.683
- 0.684
- 0.685
- 0.686
- 0.689
- 0.69
- 0.691
- 0.692
- 0.694
- 0.695
- 0.6958
- 0.696
- 0.6968
- 0.697
- 0.699
- 0.7
- 0.703
- 0.706
- 0.71
- 0.711
- 0.712
- 0.718
- 0.719
- 0.72
- 0.723
- 0.7252
- 0.726
- 0.727
- 0.728
- 0.729
- 0.7321
- 0.733
- 0.74
- 0.741
- 0.7448
- 0.745
- 0.7468
- 0.747
- 0.75
- 0.752
- 0.753
- 0.7546
- 0.755
- 0.756
- 0.7566
- 0.757
- 0.758
- 0.7595
- 0.76
- 0.762
- 0.7644
- 0.765
- 0.772
- 0.7742
- 0.775
- 0.776
- 0.7791
- 0.78
- 0.7811
- 0.782
- 0.784
- 0.785
- 0.79
- 0.791
- 0.793
- 0.7938
- 0.794
- 0.796
- 0.798
- 0.8
- 0.801
- 0.8036
- 0.804
- 0.807
- 0.81
- 0.811
- 0.812
- 0.8134
- 0.814
- 0.815
- 0.8154
- 0.816
- 0.817
- 0.82
- 0.821
- 0.8232
- 0.824
- 0.825
- 0.827
- 0.829
- 0.83
- 0.832
- 0.833
- 0.834
- 0.835
- 0.838
- 0.84
- 0.8448
- 0.845
- 0.847
- 0.848
- 0.849
- 0.85
- 0.853
- 0.854
- 0.855
- 0.856
- 0.858
- 0.86
- 0.862
- 0.863
- 0.864
- 0.867
- 0.869
- 0.87
- 0.871
- 0.8722
- 0.873
- 0.874
- 0.877
- 0.878
- 0.88
- 0.882
- 0.883
- 0.884
- 0.889
- 0.89
- 0.891
- 0.892
- 0.895
- 0.897
- 0.898
- 0.9
- 0.9016
- 0.902
- 0.904
- 0.905
- 0.909
- 0.91
- 0.9114
- 0.912
- 0.914
- 0.919
- 0.92
- 0.922
- 0.925
- 0.93
- 0.931
- 0.932
- 0.9330
- 0.934
- 0.935
- 0.94
- 0.9408
- 0.941
- 0.942
- 0.947
- 0.95
- 0.9506
- 0.951
- 0.9555
- 0.956
- 0.957
- 0.960
- 0.9604
- 0.961
- 0.962
- 0.963
- 0.968
- 0.969
- 0.9702
- 0.971
- 0.972
- 0.974
- 0.979
- 0.98
- 0.981
- 0.9829
- 0.984
- 0.985
- 0.9898
- 0.99
- 0.996
- 0.998
- 0.9996
- 1
- 1.0094
- 1.01
- 1.014
- 1.016
- 1.019
- 1.0192
- 1.02
- 1.023
- 1.028
- 1.029
- 1.03
- 1.031
- 1.034
- 1.0388
- 1.039
- 1.04
- 1.041
- 1.042
- 1.0437
- 1.044
- 1.05
- 1.052
- 1.054
- 1.059
- 1.062
- 1.065
- 1.068
- 1.0682
- 1.069
- 1.07
- 1.071
- 1.072
- 1.075
- 1.079
- 1.08
- 1.081
- 1.087
- 1.0878
- 1.089
- 1.09
- 1.096
- 1.098
- 1.099
- 1.1
- 1.105
- 1.107
- 1.1074
- 1.108
- 1.11
- 1.1172
- 1.122
- 1.127
- 1.128
- 1.13
- 1.134
- 1.14
- 1.153
- 1.159
- 1.16
- 1.166
- 1.1662
- 1.167
- 1.17
- 1.173
- 1.176
- 1.177
- 1.178
- 1.18
- 1.182
- 1.1858
- 1.187
- 1.1956
- 1.196
- 1.2
- 1.204
- 1.2054
- 1.206
- 1.21
- 1.2152
- 1.216
- 1.217
- 1.220
- 1.225
- 1.226
- 1.23
- 1.2348
- 1.236
- 1.24
- 1.2446
- 1.245
- 1.25
- 1.254
- 1.2544
- 1.255
- 1.256
- 1.26
- 1.264
- 1.2642
- 1.265
- 1.266
- 1.27
- 1.28
- 1.283
- 1.2838
- 1.285
- 1.29
- 1.2936
- 1.294
- 1.296
- 1.3
- 1.305
- 1.307
- 1.308
- 1.31
- 1.311
- 1.3132
- 1.314
- 1.32
- 1.321
- 1.327
- 1.33
- 1.3328
- 1.333
- 1.334
- 1.336
- 1.338
- 1.3426
- 1.344
- 1.349
- 1.35
- 1.36
- 1.362
- 1.365
- 1.37
- 1.374
- 1.376
- 1.379
- 1.38
- 1.381
- 1.384
- 1.387
- 1.39
- 1.398
- 1.40
- 1.4112
- 1.412
- 1.4161
- 1.417
- 1.42
- 1.421
- 1.434
- 1.439
- 1.44
- 1.445
- 1.447
- 1.45
- 1.46
- 1.467
- 1.47
- 1.471
- 1.473
- 1.4798
- 1.481
- 1.4896
- 1.491
- 1.498
- 1.499
- 1.4994
- 1.5
- 1.51
- 1.518
- 1.519
- 1.52
- 1.5288
- 1.53
- 1.5435
- 1.545
- 1.55
- 1.555
- 1.557
- 1.5582
- 1.559
- 1.5621
- 1.563
- 1.568
- 1.569
- 1.57
- 1.576
- 1.5778
- 1.579
- 1.5876
- 1.589
- 1.593
- 1.5974
- 1.598
- 1.6
- 1.61
- 1.611
- 1.613
- 1.617
- 1.618
- 1.62
- 1.625
- 1.6268
- 1.628
- 1.629
- 1.6307
- 1.631
- 1.632
- 1.64
- 1.6464
- 1.648
- 1.65
- 1.66
- 1.667
- 1.67
- 1.672
- 1.68
- 1.683
- 1.6856
- 1.686
- 1.687
- 1.689
- 1.7
- 1.707
- 1.71
- 1.713
- 1.715
- 1.72
- 1.723
- 1.73
- 1.734
- 1.7346
- 1.736
- 1.74
- 1.743
- 1.744
- 1.75
- 1.754
- 1.756
- 1.7562
- 1.76
- 1.77
- 1.771
- 1.7738
- 1.775
- 1.776
- 1.781
- 1.7836
- 1.785
- 1.79
- 1.81
- 1.821
- 1.8228
- 1.824
- 1.83
- 1.84
- 1.841
- 1.843
- 1.854
- 1.858
- 1.86
- 1.862
- 1.863
- 1.87
- 1.878
- 1.88
- 1.89
- 1.8914
- 1.893
- 1.896
- 1.9
- 1.91
- 1.911
- 1.912
- 1.9139
- 1.915
- 1.9208
- 1.922
- 1.924
- 1.927
- 1.9306
- 1.932
- 1.94
- 1.95
- 1.96
- 1.961
- 1.9698
- 1.971
- 1.9796
- 1.981
- 1.9894
- 1.99
- 1.991
- 1.994
- 1.9992
- 2.00
- 2.001
- 2.007
- 2.009
- 2.01
- 2.02
- 2.024
- 2.028
- 2.0286
- 2.03
- 2.0384
- 2.039
- 2.04
- 2.041
- 2.05
- 2.06
- 2.067
- 2.0678
- 2.069
- 2.09
- 2.0903
- 2.092
- 2.094
- 2.1
- 2.105
- 2.11
- 2.111
- 2.114
- 2.1168
- 2.117
- 2.118
- 2.130
- 2.144
- 2.15
- 2.158
- 2.16
- 2.17
- 2.175
- 2.18
- 2.192
- 2.20
- 2.202
- 2.209
- 2.21
- 2.214
- 2.22
- 2.227
- 2.23
- 2.237
- 2.245
- 2.25
- 2.26
- 2.266
- 2.27
- 2.2785
- 2.28
- 2.29
- 2.2932
- 2.295
- 2.299
- 2.3
- 2.318
- 2.320
- 2.329
- 2.332
- 2.3324
- 2.334
- 2.35
- 2.36
- 2.3618
- 2.363
- 2.39
- 2.3912
- 2.393
- 2.4
- 2.401
- 2.403
- 2.4108
- 2.412
- 2.416
- 2.4206
- 2.422
- 2.432
- 2.434
- 2.44
- 2.45
- 2.452
- 2.4696
- 2.471
- 2.489
- 2.4892
- 2.49
- 2.491
- 2.5
- 2.5088
- 2.509
- 2.511
- 2.52
- 2.5284
- 2.53
- 2.5382
- 2.54
- 2.542
- 2.548
- 2.55
- 2.5578
- 2.56
- 2.5676
- 2.569
- 2.592
- 2.6
- 2.6166
- 2.618
- 2.623
- 2.6264
- 2.628
- 2.634
- 2.638
- 2.65
- 2.654
- 2.656
- 2.672
- 2.676
- 2.697
- 2.7
- 2.7146
- 2.716
- 2.72
- 2.73
- 2.736
- 2.74
- 2.75
- 2.768
- 2.770
- 2.775
- 2.779
- 2.78
- 2.796
- 2.8
- 2.81
- 2.826
- 2.84
- 2.863
- 2.868
- 2.87
- 2.878
- 2.88
- 2.9
- 2.905
- 2.91
- 2.94
- 2.95
- 2.9694
- 2.971
- 2.99
- 3.0184
- 3.02
- 3.038
- 3.04
- 3.05
- 3.0576
- 3.06
- 3.087
- 3.089
- 3.09
- 3.1262
- 3.128
- 3.13
- 3.136
- 3.138
- 3.14
- 3.15
- 3.1654
- 3.168
- 3.1752
- 3.177
- 3.185
- 3.1948
- 3.197
- 3.200
- 3.2144
- 3.217
- 3.226
- 3.234
- 3.236
- 3.24
- 3.25
- 3.261
- 3.262
- 3.266
- 3.2732
- 3.275
- 3.2928
- 3.293
- 3.295
- 3.33
- 3.333
- 3.34
- 3.341
- 3.345
- 3.35
- 3.36
- 3.371
- 3.39
- 3.4
- 3.41
- 3.412
- 3.43
- 3.46
- 3.468
- 3.479
- 3.5
- 3.513
- 3.52
- 3.53
- 3.536
- 3.55
- 3.584
- 3.59
- 3.597
- 3.6
- 3.62
- 3.6456
- 3.648
- 3.65
- 3.660
- 3.687
- 3.73
- 3.7338
- 3.736
- 3.758
- 3.773
- 3.776
- 3.79
- 3.8
- 3.8122
- 3.815
- 3.819
- 3.82
- 3.8318
- 3.834
- 3.87
- 3.889
- 3.9004
- 3.903
- 3.92
- 3.9592
- 3.962
- 3.969
- 3.97
- 3.972
- 3.9788
- 3.981
- 3.982
- 4
- 4.018
- 4.021
- 4.04
- 4.0474
- 4.05
- 4.096
- 4.116
- 4.119
- 4.12
- 4.13
- 4.1454
- 4.148
- 4.17
- 4.182
- 4.188
- 4.23
- 4.24
- 4.26
- 4.27
- 4.287
- 4.295
- 4.31
- 4.335
- 4.34
- 4.349
- 4.36
- 4.384
- 4.4
- 4.41
- 4.419
- 4.4492
- 4.452
- 4.474
- 4.4884
- 4.489
- 4.491
- 4.5
- 4.51
- 4.52
- 4.525
- 4.55
- 4.557
- 4.56
- 4.60
- 4.61
- 4.65
- 4.68
- 4.72
- 4.74
- 4.7922
- 4.795
- 4.85
- 4.9
- 4.9098
- 4.95
- 4.9588
- 4.96
- 4.962
- 4.9784
- 4.982
- 4.99
- 5.001
- 5.0176
- 5.021
- 5.0568
- 5.06
- 5.10
- 5.1156
- 5.119
- 5.129
- 5.1352
- 5.139
- 5.1744
- 5.178
- 5.21
- 5.25
- 5.268
- 5.344
- 5.39
- 5.394
- 5.4
- 5.437
- 5.444
- 5.48
- 5.55
- 5.58
- 5.592
- 5.6
- 5.612
- 5.621
- 5.65
- 5.656
- 5.68
- 5.69
- 5.72
- 5.79
- 5.87
- 5.878
- 5.88
- 5.89
- 5.9
- 5.91
- 5.978
- 5.982
- 5.99
- 6.027
- 6.031
- 6.1152
- 6.119
- 6.174
- 6.178
- 6.18
- 6.19
- 6.2
- 6.223
- 6.227
- 6.24
- 6.272
- 6.276
- 6.3994
- 6.404
- 6.419
- 6.423
- 6.4288
- 6.433
- 6.46
- 6.464
- 6.524
- 6.533
- 6.57
- 6.6
- 6.65
- 6.68
- 6.688
- 6.718
- 6.77
- 6.99
- 7
- 7.026
- 7.06
- 7.071
- 7.1
- 7.11
- 7.16
- 7.28
- 7.35
- 7.45
- 7.4676
- 7.473
- 7.4774
- 7.482
- 7.5
- 7.6
- 7.644
- 7.649
- 7.6538
- 7.659
- 7.75
- 7.777
- 7.94
- 7.95
- 7.962
- 7.9968
- 8.002
- 8.036
- 8.041
- 8.0948
- 8.1
- 8.14
- 8.24
- 8.3
- 8.34
- 8.43
- 8.45
- 8.5
- 8.53
- 8.55
- 8.6
- 8.65
- 8.768
- 8.782
- 8.839
- 8.88
- 8.8984
- 8.904
- 8.92
- 9.01
- 9.114
- 9.12
- 9.15
- 9.22
- 9.3
- 9.32
- 9.34
- 9.4
- 9.6
- 9.9
- 10.0352
- 10.042
- 10.0548
- 10.062
- 10.1
- 10.1136
- 10.12
- 10.4
- 10.438
- 10.5
- 10.79
- 10.85
- 10.89
- 10.96
- 11.048
- 11.18
- 11.38
- 11.47
- 11.67
- 11.77
- 11.85
- 11.9
- 11.956
- 11.964
- 12.0
- 12.544
- 12.553
- 12.642
- 12.651
- 12.70
- 13.04
- 13.048
- 13.14
- 13.34
- 13.44
- 13.45
- 13.53
- 13.63
- 13.7
- 14.40
- 14.70
- 14.71
- 14.8
- 14.9352
- 14.945
- 15.05
- 15.49
- 15.59
- 15.68
- 15.691
- 16.31
- 16.67
- 16.75
- 17
- 17.4
- 17.50
- 18.63
- 18.669
- 18.682
- 19.02
- 19.50
- 19.65
- 20.1
- 20.25
- 20.5
- 21.30
- 21.57
- 22.46
- 22.9
- 23.2
- 26.48
- 26.95
- 27.10
- 29.85
- 30.45
- 33.1
- 33.75
- 36.70
- 37.45
- 56.80
-
Type
-
Allowable Load P2(N)
- 0.147
- 0.16
- 0.1764
- 0.1862
- 0.19
- 0.21
- 0.2254
- 0.23
- 0.2548
- 0.27
- 0.3038
- 0.32
- 0.3626
- 0.4
- 0.4508
- 0.49
- 0.539
- 0.54
- 0.5684
- 0.5978
- 0.62
- 0.63
- 0.637
- 0.64
- 0.686
- 0.69
- 0.7056
- 0.74
- 0.76
- 0.78
- 0.784
- 0.84
- 0.8624
- 0.88
- 0.882
- 0.9
- 0.93
- 0.931
- 0.98
- 1.029
- 1.03
- 1.078
- 1.13
- 1.14
- 1.16
- 1.176
- 1.18
- 1.27
- 1.274
- 1.32
- 1.37
- 1.372
- 1.3818
- 1.4504
- 1.47
- 1.48
- 1.51
- 1.519
- 1.52
- 1.53
- 1.57
- 1.617
- 1.62
- 1.66
- 1.67
- 1.69
- 1.715
- 1.72
- 1.7248
- 1.764
- 1.77
- 1.79
- 1.813
- 1.86
- 1.9
- 1.92
- 1.95
- 2.00
- 2.058
- 2.06
- 2.156
- 2.16
- 2.17
- 2.205
- 2.21
- 2.2148
- 2.25
- 2.254
- 2.26
- 2.3
- 2.3128
- 2.32
- 2.33
- 2.4
- 2.45
- 2.50
- 2.51
- 2.61
- 2.646
- 2.65
- 2.75
- 2.7636
- 2.79
- 2.89
- 2.891
- 2.90
- 2.9008
- 2.94
- 2.99
- 3.04
- 3.11
- 3.24
- 3.33
- 3.38
- 3.381
- 3.40
- 3.43
- 3.44
- 3.4594
- 3.53
- 3.58
- 3.626
- 3.761
- 3.773
- 3.78
- 3.82
- 3.85
- 3.90
- 3.92
- 4.067
- 4.07
- 4.165
- 4.17
- 4.22
- 4.33
- 4.36
- 4.40
- 4.41
- 4.4296
- 4.49
- 4.55
- 4.577
- 4.611
- 4.65
- 4.81
- 4.85
- 4.851
- 4.90
- 5
- 5.15
- 5.243
- 5.25
- 5.39
- 5.4
- 5.48
- 5.488
- 5.49
- 5.537
- 5.573
- 5.69
- 5.74
- 5.772
- 5.848
- 5.88
- 5.90
- 5.91
- 5.93
- 5.98
- 6.08
- 6.11
- 6.37
- 6.47
- 6.583
- 6.713
- 6.72
- 6.77
- 6.958
- 6.96
- 7.056
- 7.06
- 7.095
- 7.213
- 7.225
- 7.26
- 7.28
- 7.35
- 7.36
- 7.44
- 7.54
- 7.6
- 7.67
- 7.75
- 7.80
- 7.81
- 8.05
- 8.06
- 8.14
- 8.3
- 8.34
- 8.43
- 8.51
- 8.53
- 8.624
- 8.63
- 8.8
- 8.803
- 8.82
- 8.83
- 9.006
- 9.016
- 9.02
- 9.12
- 9.163
- 9.17
- 9.4
- 9.453
- 9.56
- 9.61
- 9.69
- 9.7
- 9.99
- 10
- 10.16
- 10.192
- 10.2
- 10.30
- 10.398
- 10.4
- 10.47
- 10.69
- 10.8
- 10.88
- 11
- 11.04
- 11.08
- 11.1
- 11.172
- 11.18
- 11.2
- 11.27
- 11.28
- 11.348
- 11.417
- 11.496
- 11.535
- 11.57
- 11.7
- 11.77
- 12
- 12.1
- 12.24
- 12.26
- 12.34
- 12.39
- 12.432
- 12.5
- 12.69
- 12.75
- 12.8
- 12.94
- 13.1
- 13.3
- 13.4
- 13.44
- 13.73
- 13.89
- 13.9
- 14
- 14.02
- 14.04
- 14.117
- 14.181
- 14.279
- 14.4
- 14.432
- 14.67
- 14.71
- 14.76
- 14.98
- 15.00
- 15.2
- 15.386
- 15.4
- 15.5
- 15.68
- 15.74
- 15.8
- 15.89
- 15.9
- 16.09
- 16.3
- 16.464
- 16.66
- 16.808
- 16.954
- 16.97
- 16.99
- 17.16
- 17.2
- 17.24
- 17.26
- 17.36
- 17.4
- 17.551
- 17.8
- 18.13
- 18.3
- 18.326
- 18.34
- 18.63
- 18.66
- 19.4
- 19.6
- 19.82
- 20.096
- 20.3
- 20.384
- 20.4
- 20.41
- 20.5
- 20.79
- 21
- 21.08
- 21.17
- 21.216
- 21.23
- 21.4
- 21.462
- 21.51
- 21.8
- 21.85
- 22.1
- 22.54
- 22.62
- 22.64
- 22.844
- 23.24
- 23.54
- 23.6
- 24
- 24.11
- 24.3
- 24.52
- 25.01
- 25.284
- 25.3
- 25.41
- 25.458
- 25.5
- 25.97
- 26
- 26.264
- 26.46
- 26.727
- 27.3
- 27.5
- 27.52
- 27.63
- 28.08
- 28.26
- 28.96
- 29.7
- 30.1
- 30.33
- 30.48
- 30.681
- 30.99
- 31
- 31.37
- 31.38
- 31.654
- 31.68
- 32.309
- 32.34
- 32.35
- 32.9
- 33
- 33.15
- 33.614
- 34.496
- 34.52
- 34.636
- 34.68
- 35.07
- 35.7
- 36.3
- 36.75
- 36.77
- 36.8
- 37.12
- 37.76
- 38.162
- 38.24
- 38.25
- 38.86
- 39.2
- 39.8
- 39.91
- 40.02
- 40.37
- 40.51
- 41.19
- 41.4
- 41.5
- 41.68
- 42.042
- 42.123
- 43.15
- 43.316
- 45.05
- 45.16
- 46.09
- 46.351
- 46.36
- 47.34
- 47.53
- 47.57
- 47.7
- 47.9
- 48
- 49.03
- 49.2
- 49.6
- 50.5
- 50.8
- 51.1
- 51.187
- 51.250
- 51.29
- 51.7
- 51.83
- 52.141
- 52.2
- 52.49
- 52.96
- 53.9
- 53.94
- 54.096
- 54.9
- 55.58
- 55.9
- 56.5
- 56.75
- 58.2
- 58.27
- 58.8
- 58.84
- 59.03
- 60.82
- 61.09
- 61.587
- 61.6
- 61.78
- 61.936
- 61.98
- 62.252
- 62.67
- 62.76
- 63.08
- 63.25
- 63.5
- 64.22
- 64.68
- 64.9
- 65.66
- 65.7
- 68.62
- 69.286
- 69.88
- 69.93
- 70.266
- 70.31
- 70.61
- 71.77
- 73.634
- 73.98
- 74.53
- 74.837
- 74.95
- 75.251
- 76
- 76.9
- 77.47
- 77.6
- 78.4
- 78.45
- 80
- 80.752
- 81.05
- 81.25
- 81.39
- 83.22
- 83.36
- 86.3
- 87.26
- 88.1
- 89.24
- 90.360
- 90.42
- 91.017
- 91.2
- 93.1
- 93.197
- 94.62
- 95.8
- 98
- 98.07
- 100.85
- 100.94
- 101.91
- 103
- 104.9
- 107
- 108.3
- 108.821
- 112.659
- 112.78
- 114.7
- 114.74
- 115.72
- 117.6
- 118.98
- 120.14
- 120.62
- 125
- 126.58
- 129.3
- 130
- 133.069
- 134.35
- 135.74
- 138.76
- 140.24
- 150.04
- 150.23
- 151.1
- 154.95
- 158.02
- 162.917
- 166.71
- 168.5
- 176.4
- 181.7
- 195.15
- 203
- 215.6
- 225.55
- 236.34
- 281.45
- 352
- 430.51
- 506
- 533
- 665
- 725
- 816
- 910
- 1049
- 1196
- 1540
- 1628
- 2285
- 2658
- 4763
-
Initial Tension Pi(N)
-
Total Number of Winding N
-
Max. Deflection(mm)
Related Categories to Tension Springs
FAQ Tension Springs
- Question: For what purpose are tension springs utilized?
- Answer: Tension springs are widely utilized in factory automation for various purposes, including maintaining tension and control in conveyor systems, balancing robotic arms for precise movements, ensuring the proper functioning of safety devices, providing force in assembly and packaging equipment, and enabling secure gripping in industrial tools. These springs play a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation, precise movement, and reliable performance in automated systems and equipment used in factory automation processes.
- Question: What distinguishes tension springs from torsion springs?
- Answer: Tension springs are designed to resist stretching forces, whereas torsion springs resist twisting or rotational forces. Tension springs extend when a force is applied, while torsion springs exert torque when twisted. Their distinct designs enable them to serve different purposes in different mechanical systems.
- Question: How do you measure the strength of a tension spring?
- Answer: Measuring the strength of a tension spring involves using a force gauge or a load cell. These tools help in gradually applying weights or loads to the suspended spring while measuring its extension. The spring rate, which represents the spring's strength, is calculated by dividing the change in force by the change in length when the spring is extended.
- Question: What are the common materials used to make tension springs?
- Answer: Tension springs are commonly made from materials like stainless steel, music wire (high-carbon steel), or various alloys. Stainless steel offers corrosion resistance, while music wire provides high strength. Alloy materials offer specific properties like heat resistance or conductivity, depending on the application requirements.
- Question: Can a tension spring be adjusted or calibrated for a specific application?
- Answer: Yes, tension springs can be adjusted or calibrated for specific applications. By altering factors like the wire diameter, numbers of turns, or length, the spring's characteristics such as force, tension, or extension can be modified. This allows for customization to match the requirements of a particular application. However, adjusting tension springs should be done carefully, considering the intended function and safety considerations.






How can we improve?
How can we improve?
Thank you for your time.
Your feedback is essential for our continuous improvement
Privacy Policy
Thank you for your cooperation.
Thank you for your time.
Your feedback is essential for our continuous improvement
Please use the inquiry form.
Privacy Policy